Соединённое Королевство Великобритании и Северной Ирландии
THE UNITED KINGDOM OF GREAT BRITAIN AND NORTHERN IRELAND
- Official name the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
- Capital London
- Area 244 000 sq. km.
- Population 60 million
- Head of the state King or Queen
- Language English
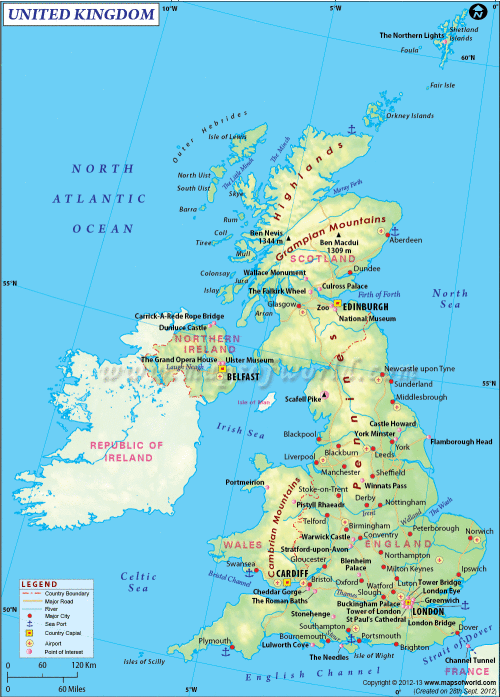
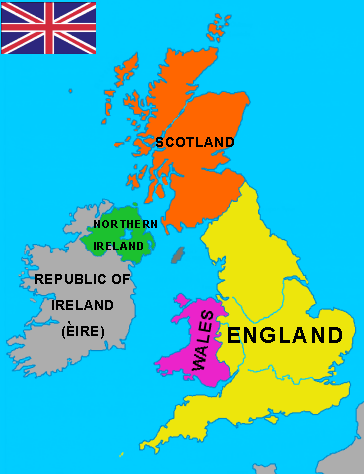
Geography. The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (the UK) consists of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland and is situated on the British Isles. The other country on the British Isles is the Republic of Ireland. The British Isles lie off the north-west coast of Europe. They consist of two large islands called Great Britain and Ireland and about 5 thousand small islands. They are washed by the Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea. The English Channel separates Great Britain from the continent. The Irish Sea separates it from Ireland.
The total area of the UK is about 244.000 square kilometers. The population is about 60 million and the country ranks about fifteenth in the world in terms of the population. 80 % of the population is urban and about 20 % of the British people are «rural dwellers». London is the capital of the whole Great Britain. The capital of Wales is Cardiff, the capital of Scotland is Edinburgh and the capital of Northern Ireland is Belfast.
The British Isles owe much to the seas. Firstly, the seas have acted as a guard and often kept the country free from wars. The shallow water is warmer than deep water and helps to keep the shores from extreme cold. And besides the shallow waters around the British Isles is the home of millions of fish.
There are neither large lakes nor long rivers there. The rivers are quite short. The longest is the Severn. The Thames is an important part of the transport network of the country. The Clyde in Scotland is a shipbuildind area. The largest lake is Lough Neagh in Northern Ireland. The Lake District known for its beauty is situated in the north-western part of England and consists of 16 lakes. The central and the southern part of England is a plain. The density of the population is the highest there. The North of Scotland is a mountainous region called the Highlands; the South of Scotland is the Lowlands. The highest peak is Ben Nevis (1342m). There are the Cambrian Mountains in the North of Wales. The highest mountain is Snowdon (1085m). The other important mountainous ranges are the Cumbrian Mountains in the North-West of England and the Cheviot Hills, which are a natural borderline between England and Scotland. The Pennines run from northern to central part of England.
Great Britain is not rich in mineral resources. There are coal deposits in Wales, in the North-East of England and in Central Scotland. Oil is extracted in the North Sea. The climate of Great Britain is generally mild and temperate. The weather tends to be changeable as a result of the winds blowing from the Atlantic and the Gulf Stream. It’s never very cold in winter, summer is generally cool.
Economy. The United Kingdom is a highly developed industrial power. It is called “the workshop of the world”, as the industrial revolution began there. The share of the industry in the Gross Domestic Product is 11 times as much as that of agriculture. The most part of the industrial and agricultural production is concentrated in England. A number of industries such as aerospace, chemicals, oil, gas, electronics and biotechnology have developed recently. The traditional industries include textile, steel production, coal-mining and shipbuilding. The largest industrial centres are London, Bristol, Manchester, Liverpool and Glasgow. For hundreds of years the overseas trade has been of vital importance to the country’s economy. Britain is a major supplier of machinery, aerospace production, chemicals, electric equipment and a growing oil exporter. Agriculture produces wheat, potatoes, fruit and vegetables. Sheep breeding has been traditionally developed.
PARTS OF THE UK
State. The United Kingdom is a constitutional monarchy. Since the age of absolute monarchy there has been a gradual decline in the Sovereign’s power and nowadays monarchs reign but do not rule. The government with the Prime Minister at the head rules the country. Parliament is the supreme legislative authority in Britain and consists of three separate elements: the Sovereign, the House of Lords and the House of Commons. The House of Commons is the lower chamber of Parliament, which consists of 650 Members of Parliament (MPs) who hold their seats during the life of Parliament (normally 5 years). The head of the House of Commons is the Speaker. The House of Lords is the upper chamber of the Parliament which is presided by the Lord Chancellor. The members of this chamber are not elected. Parliamentary government is based on the party system. It represents the executive branch of power in Britain. The party which wins most seats at a general election forms the Government and the leader of the majority party is appointed Prime Minister. The Cabinet is composed by the Prime Minister. There are about 20 ministers in it. The main opposition party forms a Shadow Cabinet and the leader of the second largest party is known as the leader of the Opposition.
The major political parties in Great Britain are: the Labour, the Conservative and the Liberal parties. The national flag of the UK is Union Jack. It consists of three red and white crosses on the blue background. They are the crosses of the patron saints of each part of the UK: England – St. George, Scotland – St. Andrew , Ireland – St. Patrick. Wales has its own flag which shows a red dragon on the white and green background. Besides, each part has its floral emblem. The rose is the emblem of England, the daffodil (or the leek) is the emblem of Wales, the thistle is the emblem of Scotland, the shamrock and the red hand are the emblems of Ireland.
FLORAL EMBLEMS OF THE UK
FLAGS OF THE UK
History. The early history of the British Isles was the history of numerous invasions. The invaders came mainly from the continent and drove the older inhabitants to the mountainous areas – Wales, Scotland and Ireland. Among the early settlers were the Celts. They probably came around 700 BC. They are the ancestors of the people in Scotland, Wales and Ireland. The national languages of these countries are of Celtic origin and differ from English. The Celts cherished nature and trees, their priests were called druids. The Romans first landed in Britain in 55 BC, but the true conquest occurred in AD 43. The Romans built about 20 towns, Londinium among them. They constructed roads and built Hadrian’s Wall to protect themselves from the warlike tribes coming from the North. Boadicca was the famous British warrior queen who raised a revolt against the Romans and burned several cities. The ruins of old Roman buildings can be seen now in Bath. The Romans left in AD 407. The next invaders were the Anglo-Saxons. They ruled the country from the 5th till the 10th century. They divided the land into administrative areas – shires, or counties and organized several kingdoms. They had the King’s Council, called Witan. Anglo – Saxons had to fight the Vikings, or the Danes. They invaded the North-East of England in the 9th century and called their kingdom Dane law. The most powerful Anglo-Saxon king of the period was Alfred the Great of Wessex, who fought the Danes successfully. He encouraged education and founded the English navy. Christianity spread at this period. Monasteries, or minsters, were the centres of learning.
In 1066 the Norman Conquest took place. William the Conqueror, the Duke of Normandy, defeated the English at the battle of Hastings and took the throne. He suppressed the Anglo-Saxon nobility and confiscated their lands. The Normans brought the feudal organization to society. At the top of it was the king surrounded by the nobles (they were the Normans); and the peasantry were at the bottom (they were of Saxon origin).
At the beginning of the 13th century the power of the English nobility was increasing. In 1215 the aristocracy forced King John to sign a document known as Magna Carta, or Great Charter. It restricted royal power and marked the beginning of constitutional government in England. In 1295 the Model Parliament was summoned.
Wars of Roses (1455-1485) was a period of political instability and trouble involving claims to the English Crown. The Dukes of Lancaster and York quarreled about who should be the king. Yorkists used the white rose as their symbol while Lancastrians used the red one. The war ended when Lancastrian Henry beat King Richard III and became the king, Henry VII.
Henry VIII (1509-1547) was ambitious and wanted to become an important influence in European politics. He rejected the power of the Pope on the pretext of remarrying. (He was notorious for having 6 wives.) Henry VIII announced himself the head of the new Anglican Church, independent of Rome. This event gave rise to a long and bloody fight between the Protestants and the Catholics.
Elizabeth I (1558-1603), Henry VIII’s daughter, reigned for 45 years. She never got married to keep the power. She did a lot to strengthen the state. Under her reign, the Spanish Armada was defeated in 1588. Elisabeth I supported Protestantism and put an end to numerous catholic plots. She had to send to the block her cousin Mary Stuart, the Queen of Scots, who supported Catholics. When Elizabeth I died childless, James VI of Scotland came to the English throne as James I in 1603. Actually England and Scotland were united under the same parliament in 1707. In the middle of the 17th century Charles I had a thirst for ruling the country without parliament. Two political parties were formed: the Cavaliers or the Royalists and the Puritan or Roundhead who stood for Parliament. Charles I attempted to arrest five MPs; in 1642 the Civil War began. The forces of Parliament defeated their enemies thanks to their leader Oliver Cromwell. In 1649 Charles I was executed. Cromwell ruled as Lord Protector from 1653 to 1658. In 1660 Charles II was restored to the throne. In 1665 the Great Plague caused many deaths in London. In 1666 the Great Fire of London took place.
The 18th century is called the Enlightenment and was the beginning of the Age of the Industrial Revolution. Isaac Newton discovered laws of gravity and optics. Francis Bacon, Adam Smith and John Lock developed philosophy and social theories. A number of engineering inventions took place: James Watt invented the steam engine in 1775; George Stephenson constructed the first locomotive in 1814; Michael Faraday discovered magneto-electricity in 1831. The Industrial Revolution led to the development of towns and to the formation of the working class. Great Britain became the leading political and industrial power in the world. Simultaneously the British Empire was formed. English seamen (Francis Drake, James Cook) made important geographic discoveries and enlarged the riches of the country.
The 19th century is often called the Victorian Age. Queen Victoria reigned for 64 years (1837-1901). Those were the years of political stability and economic prosperity. The economic and military power helped Britain to acquire new colonies. By the end of the 19th century Britain controlled the oceans and much of the land areas of the world. But this large empire was not easy to rule. The 20th century brought a lot of changes and the fall of the empire. Now most of the former British colonies make up the Commonwealth of Nations.
British National Character. One of the most striking features of British life is the self-discipline and courtesy of people of all classes. There is little noisy behaviour, and practically no loud disputing in the street. People do not rush excitedly for seats in buses or trains, but take their seats in queues at bus stops in a quiet and orderly manner. The British are naturally polite and are never tired in saying «Thank you», «I’m sorry», «Beg your pardon». If you follow anyone who is entering a building or a room, he will hold a door open for you. Many foreigners have commented on a remarkable politeness of the British people. The British don’t like displaying their emotions even in dangerous and tragic situations, and ordinary people seem to remain good-tempered and cheerful under difficulties. They don’t like any boasting or showing off in manners, dress or speech. Sometimes they conceal their knowledge: a linguist, for example, may not mention his understanding of a foreigner’s language. People abroad often have very fixed ideas about the British — they are cold, reserved, aristocratic, lazy, etc. Many people believe that half Britain is always on strike, and the other half wears a suit, a bowler hat and carries an umbrella. But the British people are different from any fixed idea you may have. One thing British people share is a love of politeness. It is important to be polite in Britain, even to people you do not know. But their politeness is not always real. English people are very tolerant, and you rarely see anyone turning round when a funny-dressed person walks through the streets. They are waiting patiently for buses, for their turn to be served. But the British do not like people who shout loudly in the street or push their way through crowds with their elbows. People don’t put on their best clothes on Sundays, but are relaxed and pleasantly untidy.
СМОТРИТЕ: Фильмы о Великобритании
Логико-смысловая схема «Соединённое Королевство»